Understanding the Basics of the Cloud : Saas, PaaS and IaaS

At the heart of cloud computing, the different “as-a-service” models are designed to deliver on-demand experiences that adapt to each organization’s needs, both in terms of functionality and team expertise. Yet, as the cloud ecosystem keeps expanding, it’s becoming harder to navigate the growing number of offerings. New models such as CaaS (Containers-as-a-Service) and FaaS (Functions-as-a-Service) are continually enriching the landscape.
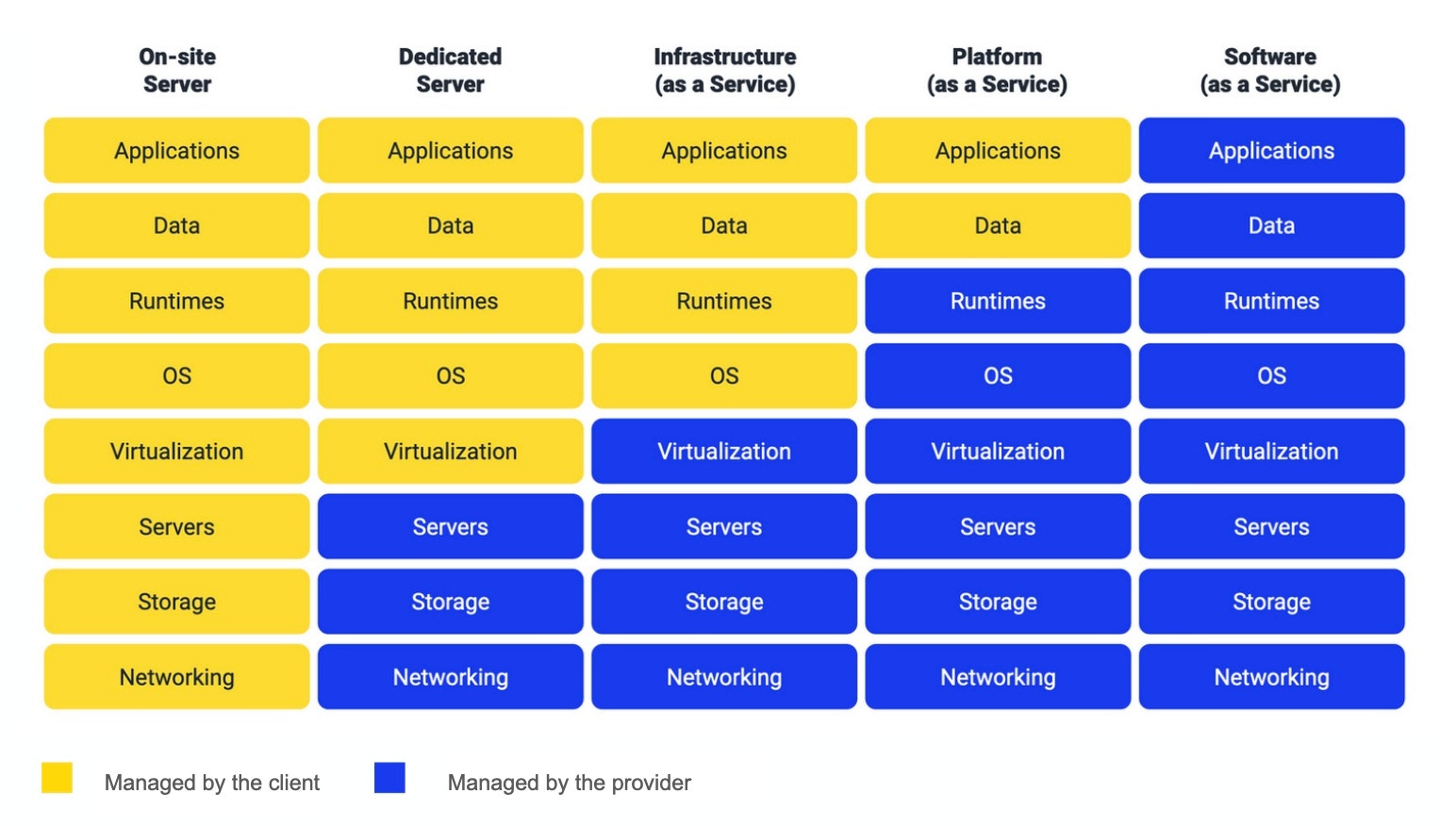
Despite this diversity, the foundation of cloud computing still rests on three main service models: PaaS (Platform-as-a-Service), SaaS (Software-as-a-Service), and IaaS (Infrastructure-as-a-Service). These are the pillars we’ll focus on today.
What is IaaS? Definition
IaaS, short for Infrastructure-as-a-Service, is the ideal option for companies that want to maintain maximum control over their cloud usage while still benefiting from the flexibility and scalability of cloud computing.
With IaaS, the cloud provider manages and maintains the physical infrastructure and data centers, delivering core infrastructure services such as storage, networking, and virtualization on demand through the cloud.
On the other hand, the customer is responsible for managing the operating system, middleware, runtimes, applications, and data.
This approach gives organizations deep control over their hosting environment, but it also requires internal teams to have the necessary technical skills and time to manage it effectively.
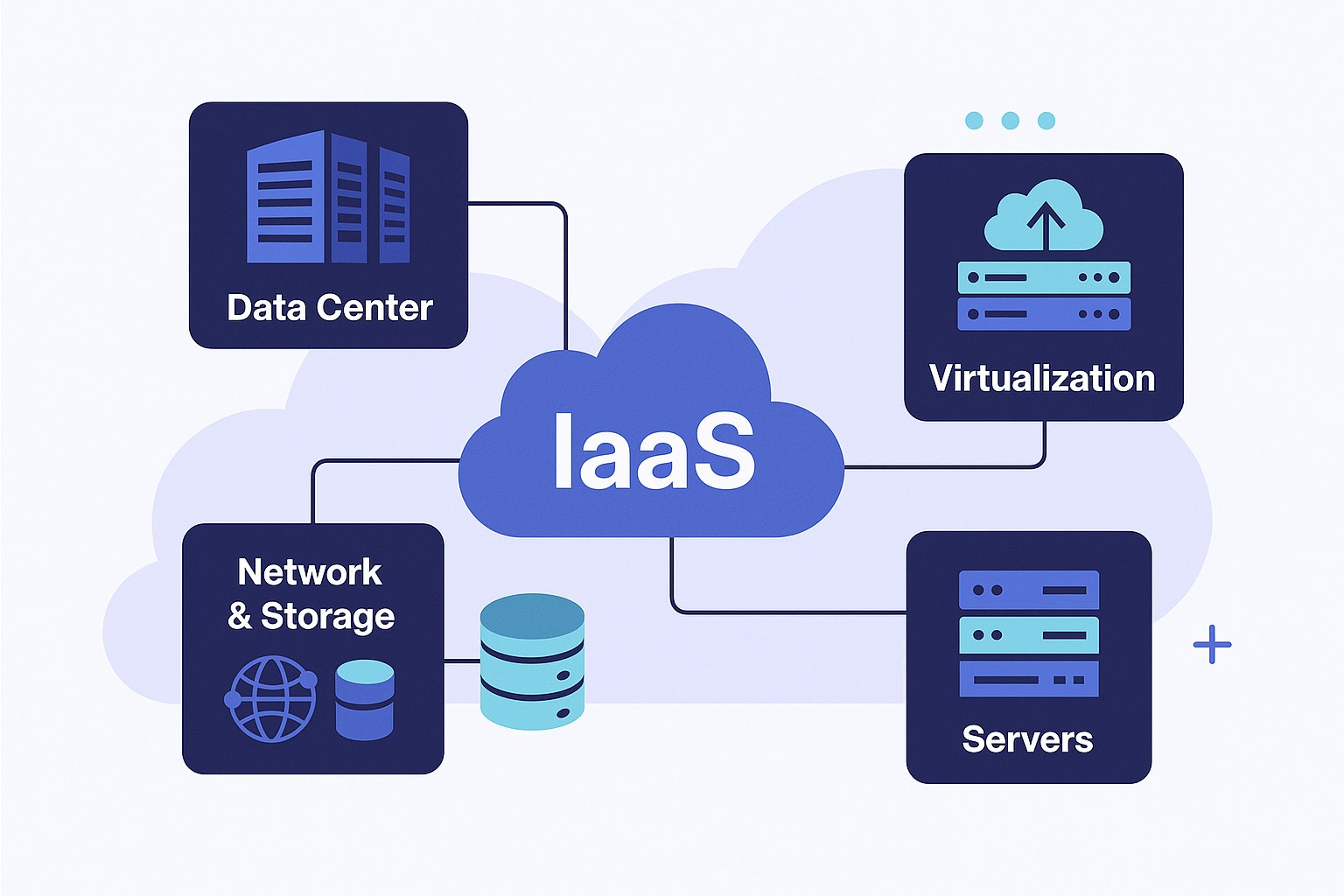
Responsibilities of the Cloud Provider:
- Virtualization
- Storage
- Servers
- Networking
Responsibilities of the Customer :
- Operating System (OS)
- Middleware
- Runtimes
- Applications
- Data
- Configuration
Benefits of IaaS
- High level of control over the cloud hosting environment
- Flexible services, with the ability to add or remove resources as needed
- More cost-effective than “on premise” infrastructure, since you only pay for what you use
Limitations of IaaS
- Data security and backups must be managed by the user
- Requires internal expertise for configuration and maintenance
Who is IaaS for?
IaaS is best suited for companies that need advanced customization options to tailor their hosting environment closely to their specific requirements. However, it does require having the internal expertise to configure and maintain the service to ensure it runs smoothly.
IaaS is therefore particularly well-suited for:
- Large enterprises that want to maintain maximum control over their application hosting
- Organizations subject to strict regulatory requirements
- Rapidly growing companies with sufficient internal technical resources looking for highly flexible hosting to support their expansion
What is PaaS? Definition
PaaS, short for Platform-as-a-Service, is the ideal solution for companies or developers who want to bring their services online as quickly as possible. In this model, the cloud provider handles most of the underlying management, including hardware, virtualization, operating systems, runtimes, storage, servers, and backups.
The user, on the other hand, is responsible for defining the necessary resources for their application and developing the code that will run on the platform.
PaaS offers a complete environment specifically designed to help developers deploy their code in an optimized setting. Instead of managing the infrastructure, teams can focus entirely on maintaining their applications and data.
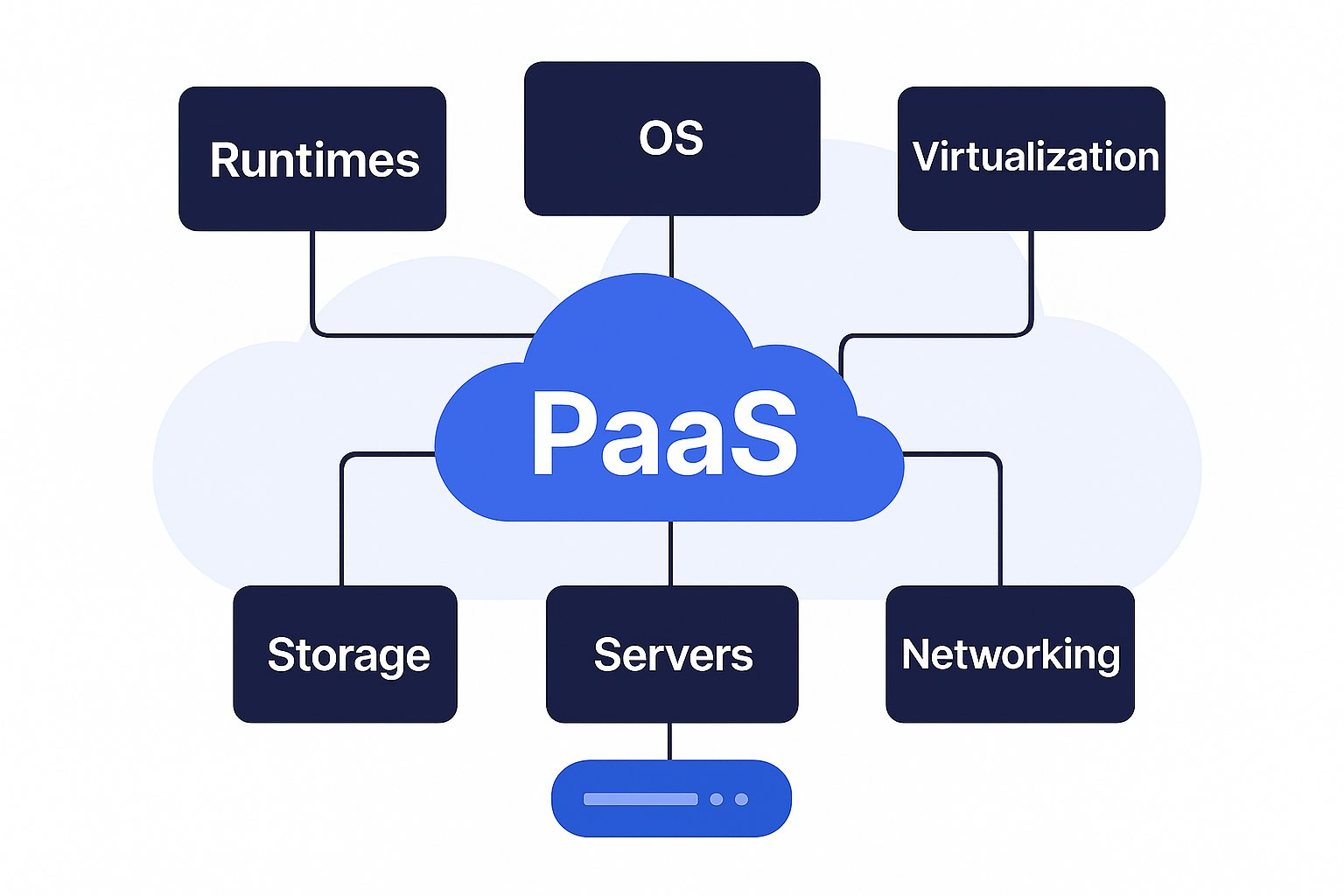
Responsibilities of the Cloud Provider:
- Virtualization
- Storage
- Servers
- Networking
- Operating system (OS)
- Middleware
- Runtimes
Responsibilities of the Customer:
- Applications
- Data
- Configuration
Benefits of PaaS
Faster time-to-market, with quick and easy application deployment
Flexible services, allowing you to add or remove resources with a single click
Cost-efficient, with pay-as-you-go pricing
Additional tools often included, such as: backups, autoscaling, database management, review apps, monitoring tools…
NoOps approach, meaning no DevOps management is required: the provider takes care of the infrastructure, platform, and all underlying components
Limitations of PaaS
Less control over the hosting environment compared to IaaS
Stack compatibility: not all PaaS providers support every programming language or database, which can limit compatibility between an application and a given platform. At Scalingo, we address this challenge with our buildpacks, which extend the platform’s capabilities and ensure compatibility with most frameworks and programming languages.
Fear of vendor lock-in: some cloud providers require the use of their proprietary tools in order to deploy on their platforms, which can make future migration difficult. At Scalingo, our commitment is simple: we rely on standardized technologies to make portability easy, and you can retrieve your data at any time.
Who is PaaS for?
The main advantage of PaaS lies in its ease of use and speed of deployment. It is therefore an ideal choice for companies looking to quickly bring their applications and updates into production, or for those that prefer to focus on high-value tasks rather than managing infrastructure. For organizations with unusual technology stacks or subject to strict regulatory requirements, it’s worth conducting some research before choosing a PaaS solution.
PaaS is particularly well-suited for:
Freelance developers and [web agencies](https://scalingo.com/blog/why-paas-is-the-best-ally-for-web-agencies), who want to deliver projects quickly to their clients
Early-stage startups and innovation teams that want to launch a proof of concept (POC) or test a new service without heavy upfront investment
Scaleups and fast-growing startups that need the flexibility and scalability of cloud hosting, without the cost or hassle of recruiting and managing a dedicated DevOps team.
Large enterprises and organizations, either as their primary cloud environment or as part of a multi-cloud strategy, to quickly test new concepts
Companies handling sensitive data, such as those in healthcare or the public sector, especially when using certified PaaS providers like Scalingo (ISO 27001, HDS, SecNumCloud IaaS layer)
What is SaaS? Definition
SaaS, short for Software-as-a-Service, refers to ready-to-use applications or services that are typically accessible through a web browser. SaaS solutions are often used alongside on-premise or cloud systems to provide additional functionality, such as accounting, HR, or project management tools. The SaaS model is also widely adopted in e-commerce, with many platforms making it easy to create and manage online stores while handling all the underlying technical aspects.
With SaaS, there’s no need to install software on every employee’s computer or manage updates: the provider takes care of everything. Users are only responsible for the data they add and manage within the application.
Benefits of SaaS
- Simple to use: no installation required, accessible directly through a web browser and/or mobile app
- Fully managed by the provider, including maintenance, updates, and infrastructure
- Minimal technical knowledge required for end users
- Predictable costs, with pay-as-you-go or subscription-based pricing models
Limitations of SaaS
Vendor lock-in and interoperability: since SaaS providers control all parts of the software, they can sometimes require the use of proprietary technologies that may not be compatible with other tools or services. This is an important factor to consider when choosing a provider.
No control over security or infrastructure, as both are fully managed by the provider
Limited customization, with fewer options to tailor the software to specific business needs
Who is SaaS for?
SaaS is suitable for any company looking to quickly start using a specific service and make it accessible to all teams, even those without technical expertise. Whether we realize it or not, most of us use SaaS applications every day, such as email, instant messaging, and other online tools.
Getting Started with PaaS on Scalingo
Convinced by what you’ve learned about PaaS? Try Scalingo, our secure, certified European PaaS that respects your data privacy and is already trusted by thousands of developers.
No server management is required: simply log in to the platform, connect your GitHub, GitLab, or Git repository, and push your code to get your application online in seconds. Check out our demo video to learn more, or get started today with 30 days free when you sign-up.
For more details about our plans, visit our pricing page or reach out to our sales team.